Target Ranges
Total Cholesterol
Total Cholesterol is a soft, fat-like, waxy substance found in the bloodstream and in all of your body’s cells. Cholesterol is an important part of a healthy body because it’s used for producing cell membranes, some hormones and serves other needed bodily functions. When there is too much cholesterol in your blood, it builds up in your arteries and can eventually increase your chances of developing heart disease.7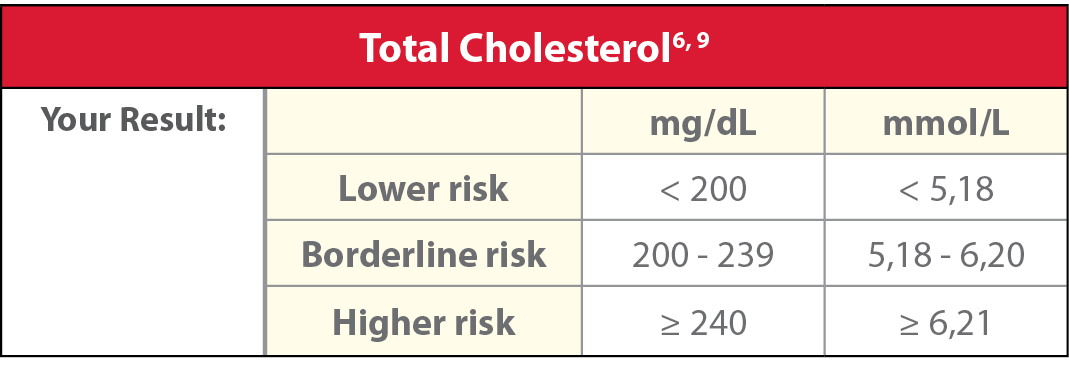
HDL Cholesterol
HDL Cholesterol is known as the “good” cholesterol because high levels of HDL can protect against heart disease. Medical experts believe HDL carries LDL cholesterol away from the arteries and removes excess cholesterol from arterial plaque, slowing its buildup. Higher HDL is desirable. Lower HDL may increase the risk of heart disease.8
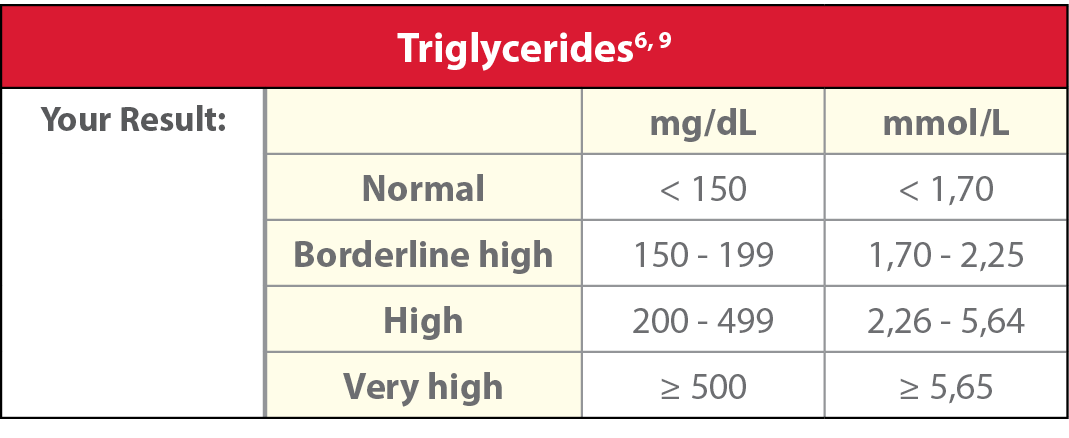
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a form of fat that the body uses to store energy. Elevated triglycerides can be due to heredity, being overweight/obese, physical inactivity, cigarette smoking, excess alcohol consumption or a diet very high in carbohydrates.8
LDL Cholesterol
LDL Cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, is a thick, hard deposit, or “plaque” that can narrow the arteries and make them less flexible. Blocked arteries in the heart can increase your risk for heart attack or stroke.8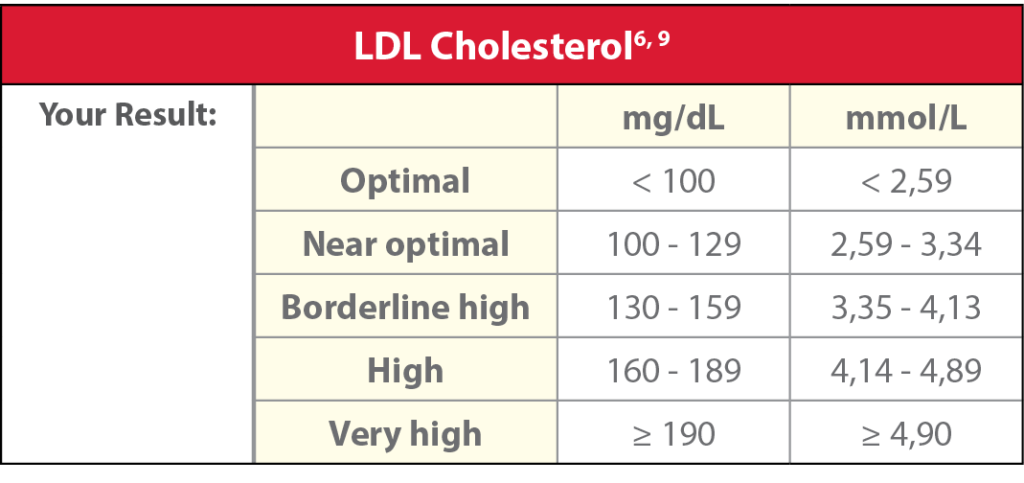
Glucose
Glucose is a type of sugar that travels through the bloodstream and is the primary source of energy for your cells. Glucose levels that remain high over time may be indicative of diabetes which can cause damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves and blood vessels.3,4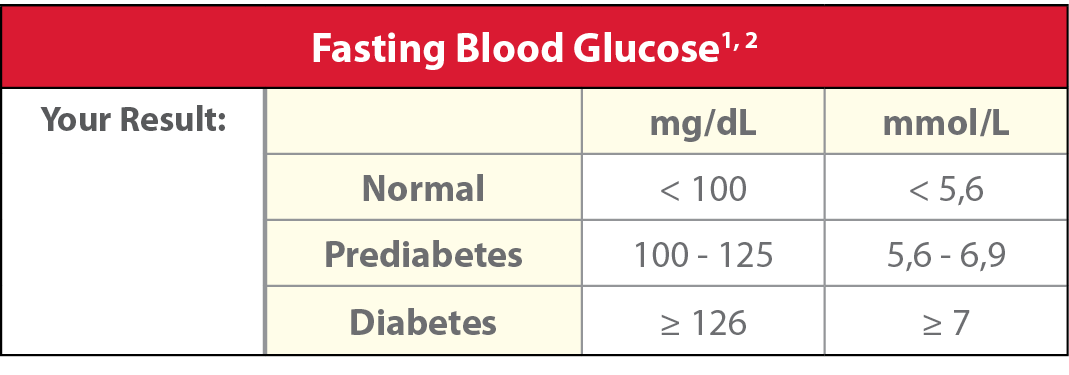
A1C
A1C is also called HbA1c or hemoglobin A1C. Hemoglobin is part of the red blood cells. The A1C complex is formed when the glucose in the blood binds irreversibly to hemoglobin (glycates). The higher the glucose level in the blood, the more that binds to the hemoglobin. Therefore, A1C values are proportional to the amount of glucose in the blood. An A1C result may be displayed in either percentage (%) units or mmol/mol units, depending on country. A1C reflects the amount of the hemoglobin that is glycated. Hemoglobin remains glycated for the lifespan of the red blood cell, about 90-120 days. Therefore, the A1C test reflects average blood glucose control for the past 2-3 months.1,3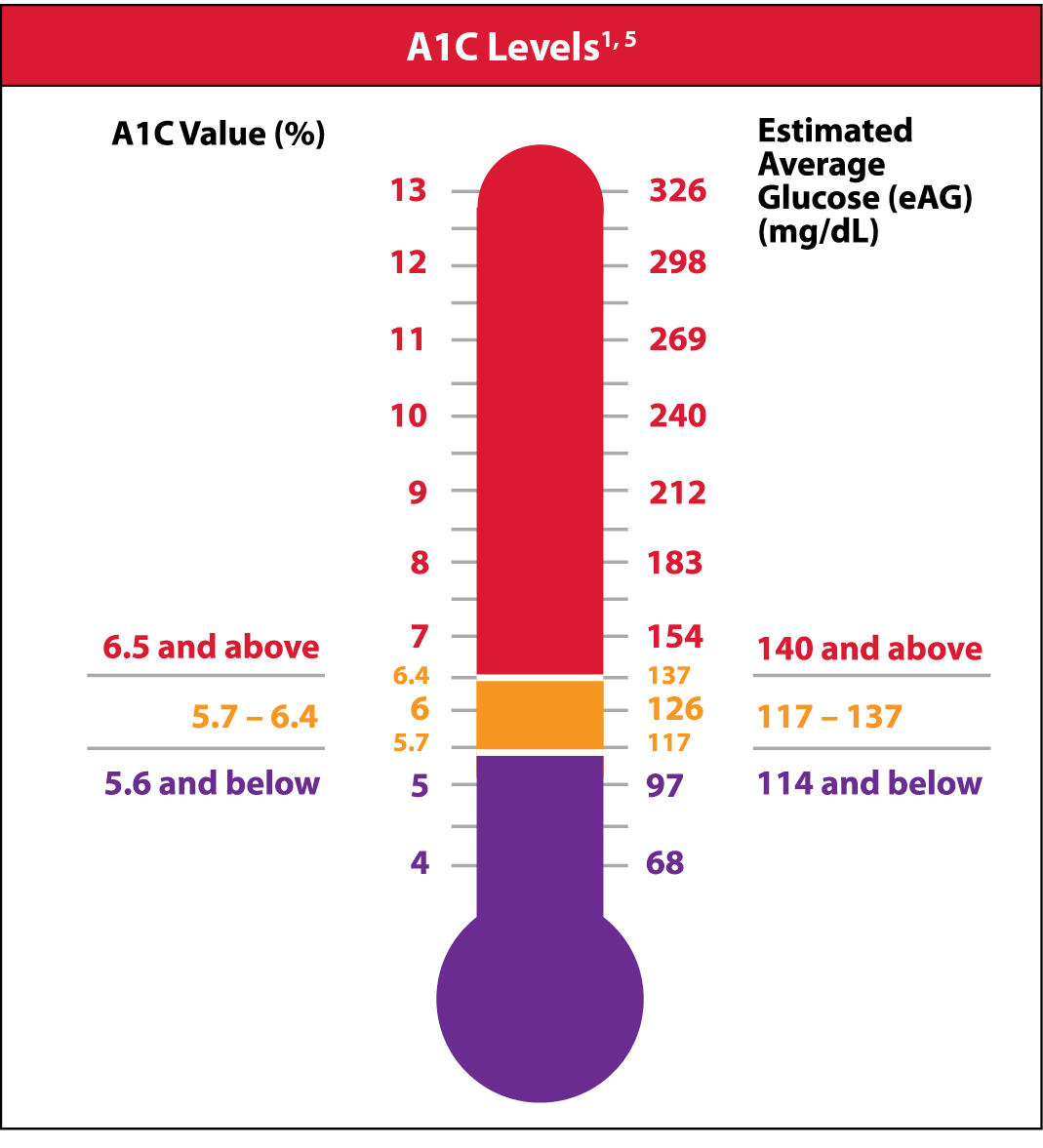
1. http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/diagnosis/
2. http://www.joslin.org/info/conversion_table_for_blood_glucose_monitoring.html
3. http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/common-terms/
4. https://www.virginiamason.org/complications
5. http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-and-care/blood-glucose-control/a1c
6. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/atglance.pdf
7. http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/Cholesterol/AboutCholesterol/About-Cholesterol_ UCM_001220_Article.jsp, http://www.news-medical.net/health/Cholesterol-Physiology.aspx
9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83505/?report=printable

